This reference sheet identifies some of the signs of learning differences and provides strategies you can use to help students reach their full potential.


written by Micaelia Randolph, EdD, MA
Educational Consultant

reviewed by Neilson Chan, PhD
Licensed Clinical Psychologist
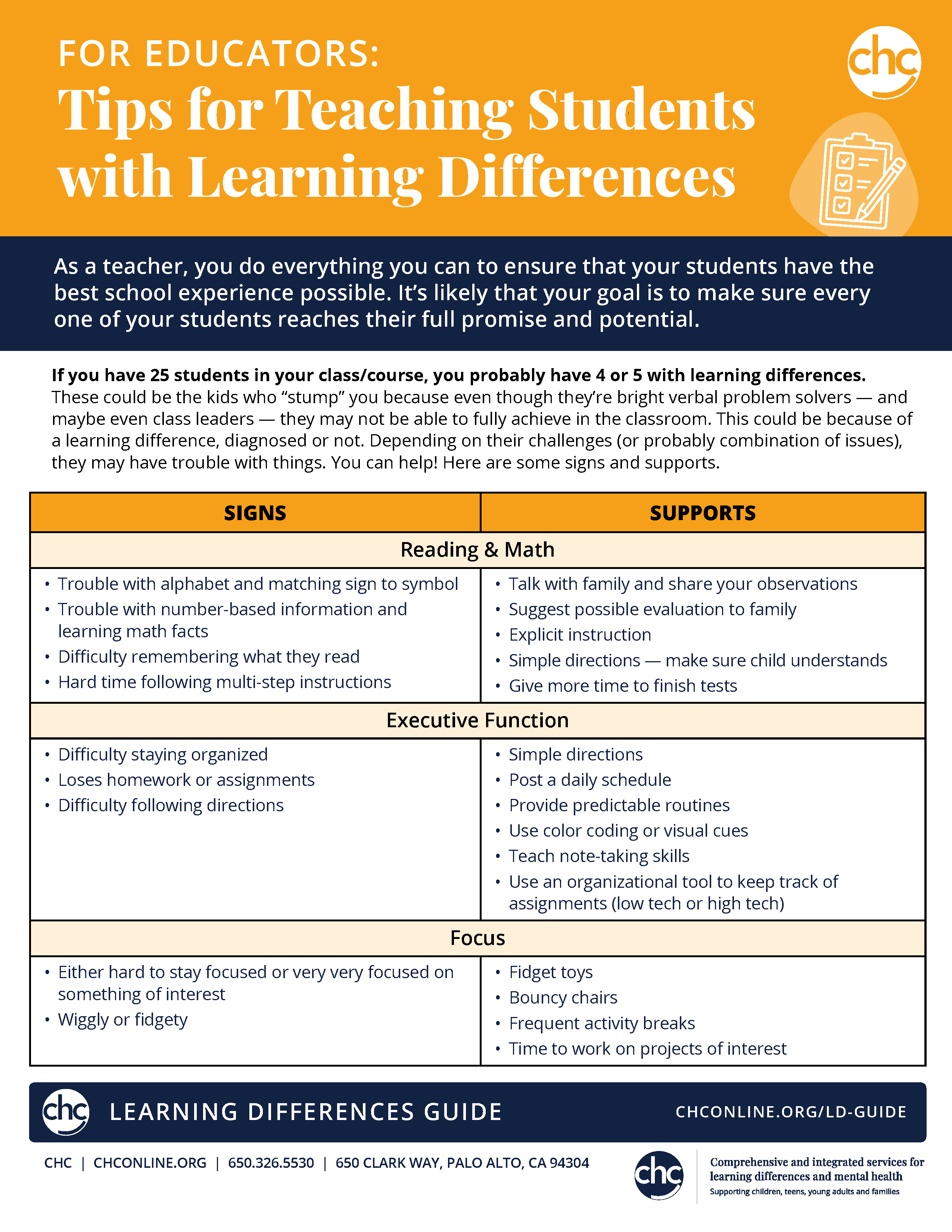
As a teacher, you do everything you can to ensure that your students have the best school experience possible. It’s likely that your goal is to make sure every one of your students reaches their full promise and potential.
Tips for Teaching Students with Learning Differences
If you have 25 students in your class/course, you probably have 4 or 5 with learning differences. These could be the kids who “stump” you because even though they’re bright verbal problem solvers—and maybe even class leaders—they may not be able to fully achieve in the classroom. This could be because of a learning difference, diagnosed or not. Depending on their challenges (or probably combination of issues), they may have trouble with things. You can help!
Download Tips for Teaching Students with Learning Differences to use offline.
|
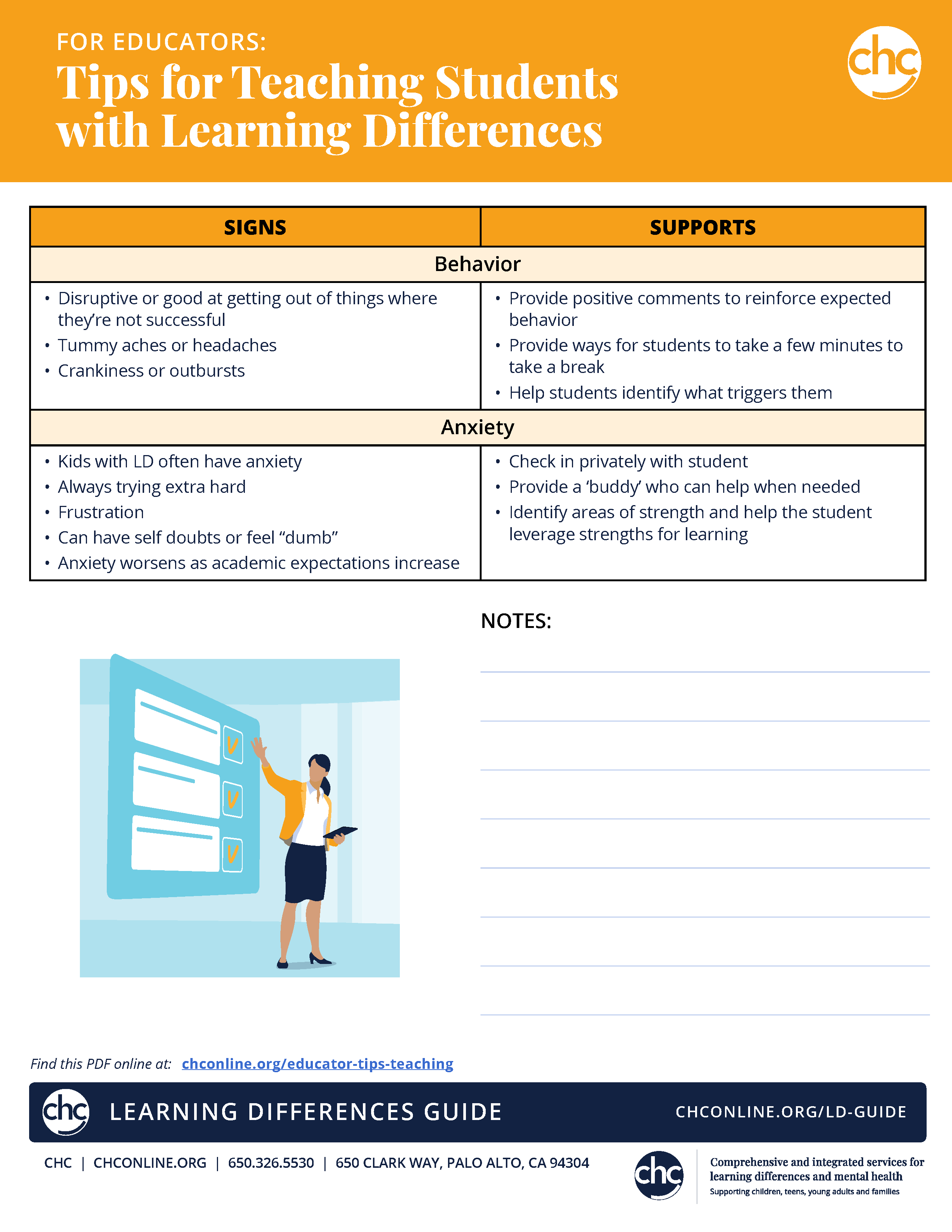
Signs |
Supports |
| Reading & Math |
|
|
|
| Executive Function |
|
|
|
| Focus |
|
|
|
| Behavior |
|
|
|
| Anxiety |
|
|
|
This resource is part of CHC’s Learning Differences Guide.
Download a PDF of Tips for Teaching Students with Learning Differences. See CHC’s Learning Differences Guide for more resources on this topic.